AI-Powered Analysis
Learn how to use Noir's AI integration to get advanced analysis of your code. This guide covers the necessary flags and options for connecting to LLM providers like OpenAI, xAI, and local models.
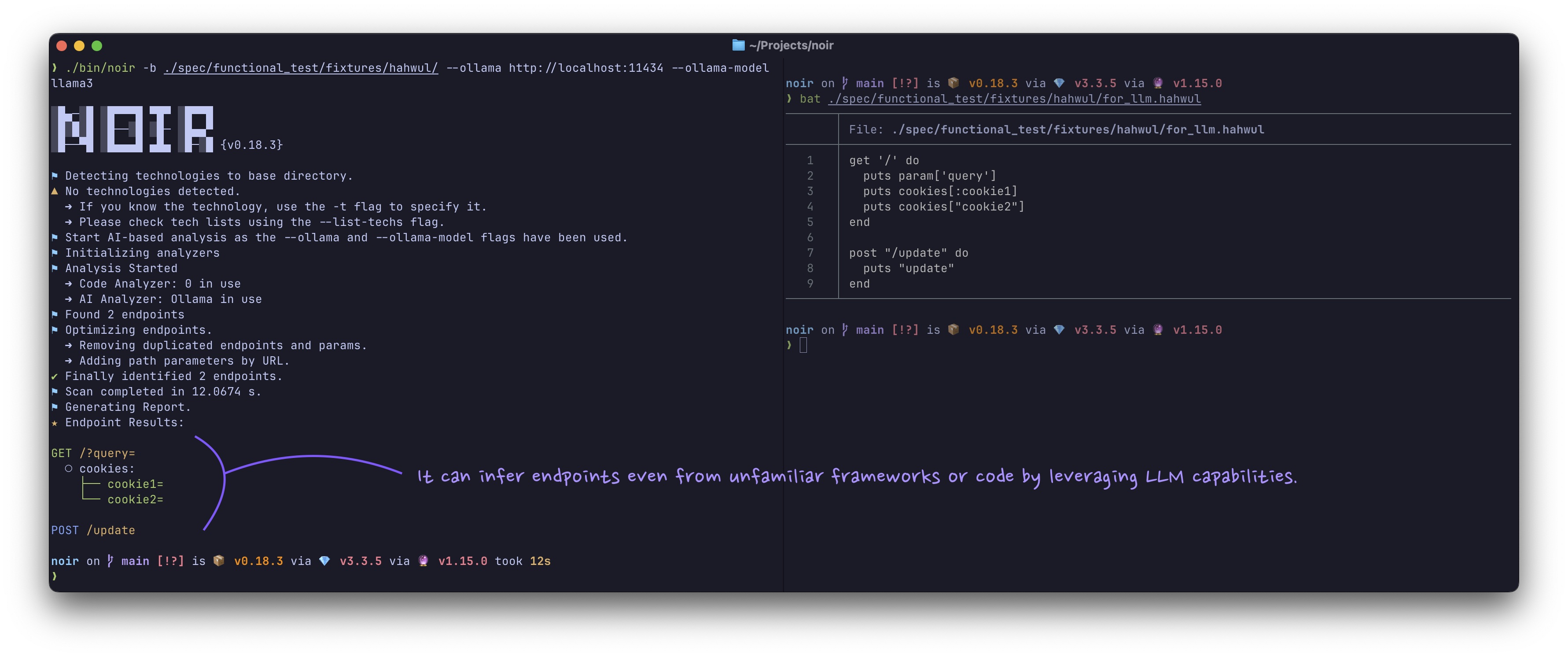
Connect Noir to Large Language Models (cloud-based or local) for deeper code analysis. AI helps identify endpoints in unsupported languages and frameworks.
Usage
Specify an AI provider, model, and API key:
noir -b . --ai-provider <PROVIDER> --ai-model <MODEL_NAME> --ai-key <YOUR_API_KEY>Command-Line Flags
--ai-provider: AI provider prefix (e.g.,openai,ollama) or custom API URL--ai-model: Model name (e.g.,gpt-4o)--ai-key: API key (or useNOIR_AI_KEYenvironment variable)--ai-max-token: Maximum tokens for AI requests (optional)--cache-disable: Disable LLM cache--cache-clear: Clear LLM cache before run
AI responses are cached on disk by default to speed up analysis and reduce costs.
Supported AI Providers
Noir has built-in presets for several popular AI providers:
| Prefix | Default Host |
|---|---|
openai | https://api.openai.com |
xai | https://api.x.ai |
github | https://models.github.ai |
azure | https://models.inference.ai.azure.com |
vllm | http://localhost:8000 |
ollama | http://localhost:11434 |
lmstudio | http://localhost:1234 |
For custom providers, use the full API URL: --ai-provider=http://my-custom-api:9000.
Benefits and Considerations
- Expanded Support: Analyze unsupported frameworks and languages
- Deeper Insights: Identify subtle or complex endpoints
- Trade-offs: May produce false positives and slower performance
How AI-Powered Analysis Works
Noir's AI integration follows a sophisticated workflow that combines intelligent file filtering, optimized bundling, response caching, and endpoint optimization to deliver comprehensive analysis results.
flowchart TB
Start([Start AI Analysis]) --> InitAdapter[Initialize LLM Adapter]
InitAdapter --> ProviderCheck{Provider Type?}
ProviderCheck -->|OpenAI/xAI/etc| GeneralAdapter[General Adapter<br/>OpenAI-compatible API]
ProviderCheck -->|Ollama/Local| OllamaAdapter[Ollama Adapter<br/>with Context Reuse]
GeneralAdapter --> FileSelection
OllamaAdapter --> FileSelection
FileSelection[File Selection] --> FileCount{File Count?}
FileCount -->|≤ 10 files| AnalyzeAll[Analyze All Files]
FileCount -->|> 10 files| LLMFilter[LLM-Based Filtering]
LLMFilter --> CacheCheck1{Cache Hit?}
CacheCheck1 -->|Yes| UseCached1[Use Cached Filter]
CacheCheck1 -->|No| FilterLLM[Call LLM with<br/>FILTER prompt]
FilterLLM --> StoreCache1[Store in Cache]
UseCached1 --> TargetFiles
StoreCache1 --> TargetFiles
TargetFiles[Selected Target Files] --> BundleCheck{Large File Set<br/>and Token Limit?}
AnalyzeAll --> BundleCheck
BundleCheck -->|Yes| BundleMode[Bundle Analysis Mode]
BundleCheck -->|No| SingleMode[Single File Mode]
BundleMode --> CreateBundles[Create File Bundles<br/>within Token Limits]
CreateBundles --> ParallelBundles[Process Bundles<br/>Concurrently]
ParallelBundles --> BundleLoop{For Each Bundle}
BundleLoop --> CacheCheck2{Cache Hit?}
CacheCheck2 -->|Yes| UseCached2[Use Cached Analysis]
CacheCheck2 -->|No| BundleLLM[Call LLM with<br/>BUNDLE_ANALYZE prompt]
BundleLLM --> StoreCache2[Store in Cache]
UseCached2 --> ParseEndpoints1
StoreCache2 --> ParseEndpoints1
ParseEndpoints1[Parse Endpoints<br/>from Response] --> BundleLoop
BundleLoop -->|Done| Combine
SingleMode --> FileLoop{For Each File}
FileLoop --> CacheCheck3{Cache Hit?}
CacheCheck3 -->|Yes| UseCached3[Use Cached Analysis]
CacheCheck3 -->|No| AnalyzeLLM[Call LLM with<br/>ANALYZE prompt]
AnalyzeLLM --> StoreCache3[Store in Cache]
UseCached3 --> ParseEndpoints2
StoreCache3 --> ParseEndpoints2
ParseEndpoints2[Parse Endpoints<br/>from Response] --> FileLoop
FileLoop -->|Done| Combine
Combine[Combine All Endpoints] --> LLMOptCheck{LLM Optimization<br/>Enabled?}
LLMOptCheck -->|Yes| FindCandidates[Find Optimization<br/>Candidates]
FindCandidates --> OptLoop{For Each Candidate}
OptLoop --> OptimizeLLM[Call LLM with<br/>OPTIMIZE prompt]
OptimizeLLM --> ApplyOpt[Apply Optimizations<br/>to Endpoint]
ApplyOpt --> OptLoop
OptLoop -->|Done| FinalResults
LLMOptCheck -->|No| FinalResults[Final Optimized Results]
FinalResults --> End([End])
style Start fill:#e1f5e1
style End fill:#e1f5e1
style LLMFilter fill:#fff4e1
style FilterLLM fill:#e1f0ff
style BundleLLM fill:#e1f0ff
style AnalyzeLLM fill:#e1f0ff
style OptimizeLLM fill:#e1f0ff
style CacheCheck1 fill:#ffe1e1
style CacheCheck2 fill:#ffe1e1
style CacheCheck3 fill:#ffe1e1
style UseCached1 fill:#e1ffe1
style UseCached2 fill:#e1ffe1
style UseCached3 fill:#e1ffe1
Key Components
1. LLM Adapter Layer
Noir uses a provider-agnostic adapter pattern that supports multiple LLM providers:
- General Adapter: For OpenAI-compatible APIs (OpenAI, xAI, Azure, GitHub Models, etc.)
- Ollama Adapter: Specialized adapter with server-side context reuse for improved performance
2. Intelligent File Filtering
When analyzing projects with many files (>10), Noir uses the LLM to intelligently filter which files are likely to contain endpoints:
- Sends file path list to LLM with FILTER prompt
- LLM identifies potential endpoint files
- Reduces analysis time and costs
3. Bundle Analysis
For large codebases, Noir bundles multiple files together to maximize efficiency:
- Estimates token usage for each file
- Creates bundles within model token limits (with 80% safety margin)
- Processes bundles concurrently for speed
- Uses BUNDLE_ANALYZE prompt to extract endpoints from all files in bundle
4. Response Caching
All LLM responses are cached on disk to improve performance and reduce costs:
- Cache key: SHA256 hash of (provider + model + operation + format + payload)
- Cache location:
~/.local/share/noir/cache/ai/(orNOIR_HOMEif set) - Enables instant re-analysis of unchanged code
- Can be disabled with
--cache-disableor cleared with--cache-clear
5. LLM Optimizer
An optional post-processing step that refines endpoint results:
- Identifies non-standard patterns (wildcards, unusual naming, etc.)
- Normalizes URLs and parameter names
- Applies RESTful conventions
- Improves overall endpoint quality

